Hardy Weinberg Problem Set - Hardy Weinberg Problem Set / As with any other type of mathematics the best way to master a new skill is by practice.
Hardy Weinberg Problem Set - Hardy Weinberg Problem Set / As with any other type of mathematics the best way to master a new skill is by practice.. However, for individuals who are unfamiliar with algebra, it takes some practice working problems before you get the hang of it. Use the hardy weinberg equation to determine the allele frequences of traits in a dragon population. P added to q always equals one (100%). Below is a data set on wing coloration in the scarlet tiger moth (panaxia dominula). In a population with two alleles for a certain locus, b and b, the allele frequency of b is 0.7.
Some basics and approaches to solving problems. The genotypes are given in the problem description: In a population with two alleles for a certain locus, b and b, the allele frequency of b is 0.7. However, for individuals who are unfamiliar with algebra, it takes some practice working problems before you get the hang of it. P2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 p + q = 1 p = frequency of the dominant allele in the population q = frequency of the recessive.
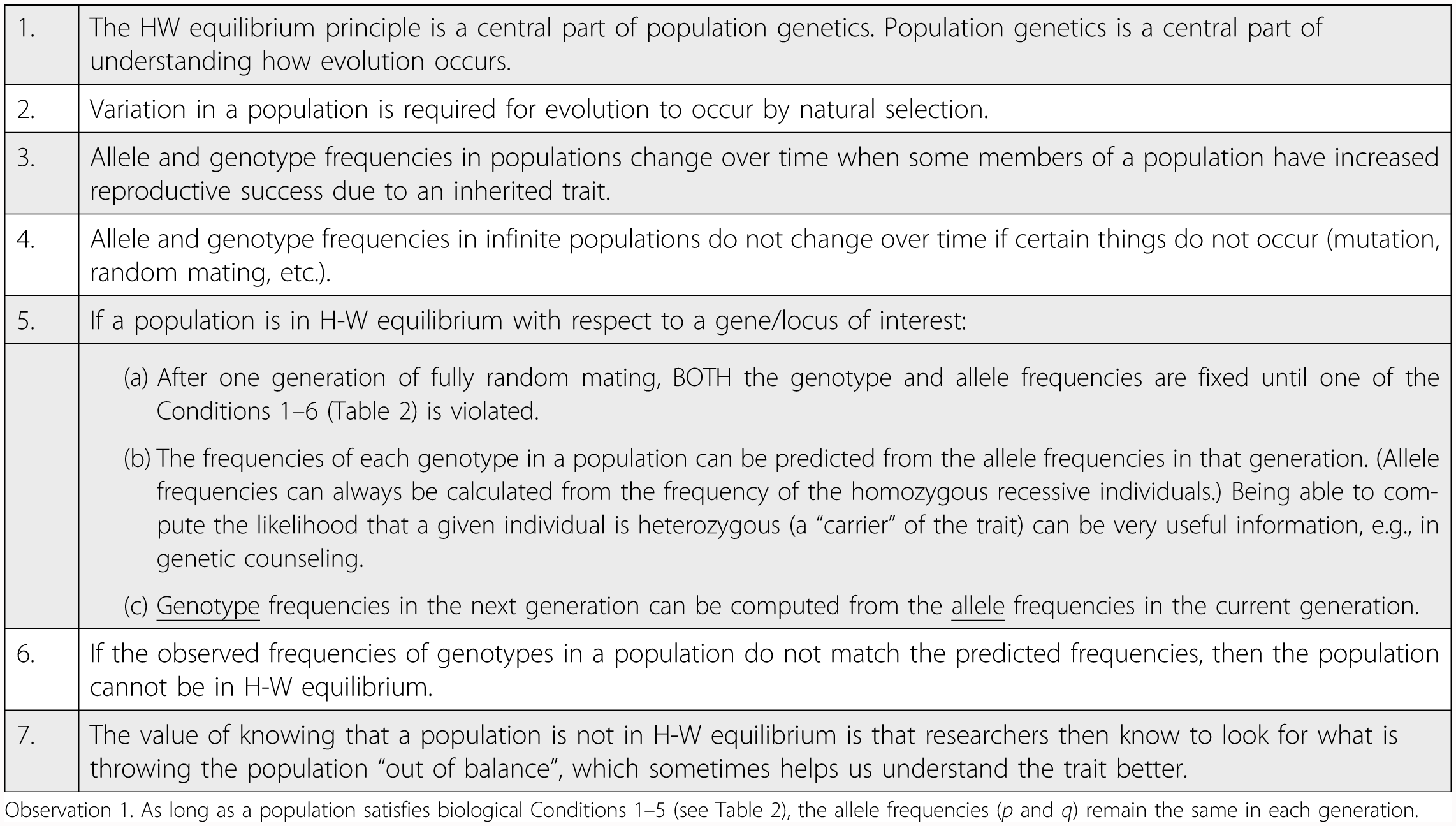
This is a classic data set on wing coloration in the scarlet tiger moth (panaxia dominula).
The principle behind it is that, in a population where certain conditions are met (see below), the frequency of the. The horizontal axis shows the two allele frequencies p and q and the everything is set equal to 1 because all individuals in a population equals 100 percent. As with any other type of mathematics the best way to master a new skill is by practice. The genotypes are given in the problem description: Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Follow up with other practice problems using human hardy weinberg problem set. What is the frequency of heterozygotes aa in a randomly mating population in which the frequency of all dominant phenotypes is 0.19? The frequency of two alleles in a gene pool is 0.19 (a) and 0.81(a). These frequencies will also remain constant for future generations. What are the expected frequencies of the three genotypes in this population? P2+2pq+q2 = 1, where 'p' and 'q' represent the frequencies of alleles. Individuals producing seed without an awn are homozygous recessive, those with a long awn are homozygous dominant, and those with a medium awn are heterozygous. P2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 p + q = 1 p = frequency of the dominant allele in the population q = frequency of the recessive.
Use the hardy weinberg equation to determine the allele frequences of traits in a dragon population. Some or all of these types of forces all act on living populations at various times and evolution at some level occurs in all living organisms. The horizontal axis shows the two allele frequencies p and q and the everything is set equal to 1 because all individuals in a population equals 100 percent. Below is a data set on wing coloration in the scarlet tiger moth (panaxia dominula). Start studying hardy weinberg problem set.

Answer key hardy weinberg problem set p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 and p + q = 1 p = frequency of the dominant allele in the population q = frequency of the recessive allele in the 2pq = 2(.98)(.02) =.04 7.
Some basics and approaches to solving problems. This is a classic data set on wing coloration in the scarlet tiger moth (panaxia dominula). However, for individuals who are unfamiliar with algebra, it takes some practice working problems before you get the hang of it. In a population with two alleles for a certain locus, b and b, the allele frequency of b is 0.7. Speaking of nerds, please forgive the annoying sound buzzes and glitches. As with any other type of mathematics the best way to master a new skill is by practice. The frequency of two alleles in a gene pool is 0.19 (a) and 0.81(a). P2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 p + q = 1 p = frequency of the dominant allele in the population q = frequency of the recessive. P added to q always equals one (100%). My goal is to be able to solve the following kind of problem. The genotypes are given in the problem description: If given frequency of dominant phenotype. Below is a data set on wing coloration in the scarlet tiger moth (panaxia dominula).
However, for individuals who are unfamiliar with algebra, it takes some practice working problems before you get the hang of it. P2+2pq+q2 = 1, where 'p' and 'q' represent the frequencies of alleles. These data sets will allow you to practice. The principle behind it is that, in a population where certain conditions are met (see below), the frequency of the. Therefore, the number of heterozygous individuals 3.

I will post answers to these problems in a week or two.
Some basics and approaches to solving problems. Use the hardy weinberg equation to determine the allele frequences of traits in a dragon population. Some or all of these types of forces all act on living populations at various times and evolution at some level occurs in all living organisms. These data sets will allow you to practice. This set is often saved in the same folder as. P2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 p + q = 1 p = frequency of the dominant allele in the population q = frequency of the recessive. However, for individuals who are unfamiliar with algebra, it takes some practice working problems before you get the hang of it. What is the frequency of heterozygotes aa in a randomly mating population in which the frequency of all dominant phenotypes is 0.19? If given frequency of dominant phenotype. Grab a calculator and join me for a bit of practice with hardy weinberg problems, exercises, implements of torture or just good nerd fun! The principle behind it is that, in a population where certain conditions are met (see below), the frequency of the. What assumption(s) did you make to solve this problem? Start studying hardy weinberg problem set.
Komentar
Posting Komentar